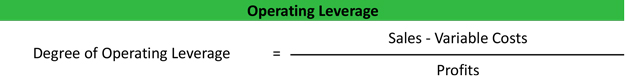Higher measures of leverage mean that a company’s operating income is more sensitive to sales changes. Managers need to monitor DOL to adjust the firm’s pricing structure towards higher sales volumes as a small decrease in sales can lead to a dramatic decrease in profits. The degree of operating leverage calculator shows the effect on operating income of the cost structure of a business. The degree of operating leverage can never be harmful since it is a two-positive numbers ratio, i.e., sales and operating income. Moreover, the negative operating leverage implies that the operating income decreases as the revenue increases, which is inconsistent with the traditional definition of operating leverage.
What Is the Difference Between Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage?
If the firm generates adequate sales volumes, fixed costs are covered, thereby leading to a profit. If fixed costs are higher in proportion to variable costs, a company will generate a high operating leverage ratio and the firm will generate a larger profit from each incremental sale. A larger proportion of variable costs, on the other hand, will generate a low operating leverage ratio and the firm will generate a smaller profit from each incremental sale. In other words, high fixed costs means a higher leverage ratio that turn into higher profits as sales increase. This is the financial use of the ratio, but it can be extended to managerial decision-making.
Can I Use DOL to Compare Different Companies?
- Most of Microsoft’s costs are fixed, such as expenses for upfront development and marketing.
- By calculating the DOL, you can understand how fixed costs influence your business profitability.
- Use the calculator as a strategic tool for enhancing your financial planning efforts.
- This example indicates that the company will have different DOL values at different levels of operations.
Therefore, the company can make changes to increase operating profits accordingly. However, companies that need to spend a lot of money on property, plant, machinery, and distribution channels, cannot easily control consumer demand. So, in the case of an economic downturn, their earnings may plummet because of their high fixed costs and low sales. It is important to understand the concept of the DOL formula because it helps a company appreciate the effects of operating leverage on the probable earnings of the company. It is a key ratio for a company to determine a suitable level of operating leverage to secure the maximum benefit out of a company’s operating income.
What is Degree of Operating Leverage – Its Formula, Calculation and What Does It Measure
If a firm generates a high gross margin, it also generates a high DOL ratio and can make more money from incremental revenues. This happens because firms with high degree of operating leverage (DOL) do not increase costs proportionally to their sales. On the other hand, a high DOL incurs a higher forecasting risk because even a small forecasting error in sales may lead to large miscalculations of the cash flow projections. Therefore, poor managerial decisions can affect a firm’s operating level by leading to lower sales revenues.
How Does Operating Leverage Impact Break-Even Analysis?
Yes, DOL can be used to compare the operational risk of companies within the same industry, helping investors identify firms with higher or lower financial risk profiles. Alternatively, a company with a low DOL typically spends more money on fixed assets to increase its sales. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
What is your current financial priority?
A high DOL indicates that a company has a larger proportion of fixed costs compared to variable costs. This suggests that the company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are highly journal entry for purchase returns returns outward example sensitive to changes in sales. When sales increase, a company with high operating leverage can see significant boosts in operating income due to the fixed nature of its costs.
Actually, it can mean that the business is deteriorating or going through a bad economic cycle like the one from the 2nd quarter of 2020. If you try different combinations of EBIT values and sales on our smart degree of operating leverage calculator, you will find out that several messages are displayed. For example, a DOL of 2 means that if sales increase (decrease) by 50%, operating income is expected to increase (decrease) by twice, i.e., 100%. The following information pertains to last week’s operations of XYZ Company.
The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) indicates how sensitive a company’s operating income is to changes in sales volume. The degree of operating leverage calculator is a tool that calculates a multiple that rates how much income can change as a consequence of a change in sales. In this article, we will learn more about what operating leverage is, its formula, and how to calculate the degree of operating leverage. Furthermore, from an investor’s point of view, we will discuss operating leverage vs. financial leverage and use a real example to analyze what the degree of operating leverage tells us.
When planning for business growth or expansion, knowing your DOL is crucial. Use the calculator to assess the risk and reward trade-offs for your growth strategies. As a hypothetical example, say Company X has $500,000 in sales in year one and $600,000 in sales in year two. In year one, the company’s operating expenses were $150,000, while in year two, the operating expenses were $175,000.
Operating Leverage is controlled by purchasing or outsourcing some of the company’s processes or services instead of keeping it integral to the company. Another way to control this operational expense line item is to reduce unnecessary expenses, especially during slow seasons when sales are low. The only difference now is that the number of units sold is 5mm higher in the upside case and 5mm lower in the downside case. Companies with high DOLs have the potential to earn more profits on each incremental sale as the business scales. A company with a high DOL coupled with a large amount of debt in its capital structure and cyclical sales could result in a disastrous outcome if the economy were to enter a recessionary environment. The DOL would be 2.0x, which implies that if revenue were to increase by 5.0%, operating income is anticipated to increase by 10.0%.
A company with high financial leverage is riskier because it can struggle to make interest payments if sales fall. By analyzing DOL, stakeholders can better anticipate the impacts of sales fluctuations on a company’s profitability. Finally the calculator uses the formulas above to calculate the DOL and the operating leverage for each business. Use the DOL calculation to support pricing decisions for your products or services. A higher DOL suggests that any price changes will have a magnified effect on your profits. Determine the optimal pricing strategy by considering the DOL and its implications.